-
Homepage
-
Sealing knowledge
- How are seals and gaskets manufactured?
How are seals and gaskets manufactured?
Have you ever wondered exactly how seals are manufactured and which materials are processed in what way? Here at Kofler - Dichtungen, we show you the most common modern methods for the production of seals and gaskets: from high-precision computer-controlled customization to mass production using injection molding machines.
You will receive a comprehensive overview of which elastomer materials can be processed and which methods can be applied for the series sizes of seals and seal sets relevant to you. Here, read about our sealing know-how and learn in which industries our seals are used.

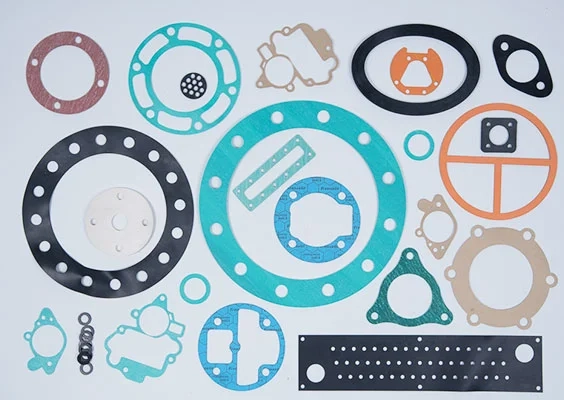
Twisted seals
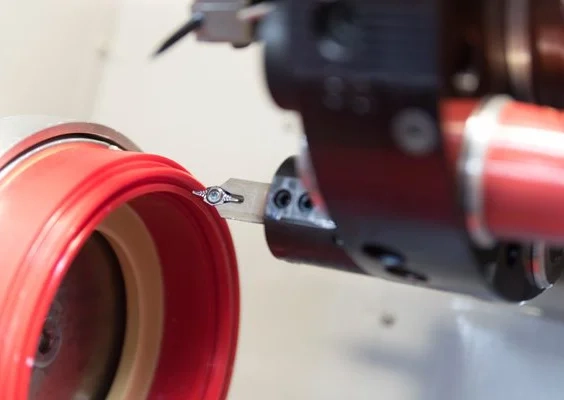
Twisted seals are cut from a blank using a CNC lathe. If the measurement of an existing seal succeeds precisely enough, seals can be made according to samples.
The turning process itself is computer-controlled and automatic. Once programmed, many workpieces can be produced with little personnel effort. Since this lathe can be flexibly adjusted to workpieces, there are no additional tool costs.
This process is suitable for a large number of materials, including plastics and rubber. It is therefore also ideally suited for the production of high-precision piston seals, and rod seals for applications in hydraulics and as a hydraulic cylinder seal.

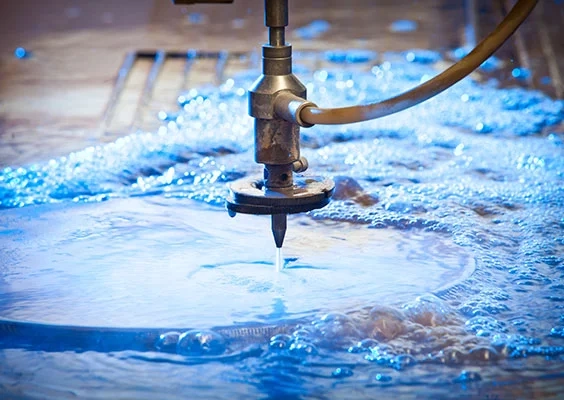
Waterjet-Cut Sealing Elements
When water jet cutting, a thin water jet (< 1 mm / 0.039 in) is directed at the workpiece with very high pressure. Depending on the hardness of the material, abrasive additives (e.g. sand) may be added to the water, but this is not necessary for plastic seals. The high kinetic energy of the water removes material, whereby the workpiece does not heat up significantly.
These properties make the waterjet cutting technique a very suitable method for cutting seals from soft, elastic plastics. The cut edges are very straight, as the material is not pressed or deformed during the cut. As already mentioned, this is an advantage over punching out seals. However, with some materials, this method can form unsightly fringes and residues on the sealing edge.
The nozzle of the water jet cutting machine is aligned in a CNC-controlled manner, so that the cutting process can proceed fully automatically. This makes the production of larger quantities cheaper. In addition, there are no additional tool costs.

Plotted seals
Plotted seals are cut out of a plate with a CNC-controlled cutting plotter with a movable blade. Thus, seals can be produced to individual dimensions with only one machine, so that no additional tool costs are incurred. This procedure takes place automatically after programming on the computer and requires only a small number of personnel after the first programming.
Due to the process, the plotting of seals is particularly suitable for relatively soft materials in small material thicknesses. It is ideally suited for the production of flat gaskets in small series.
The cutting depth can also be set with high precision, so that, for example, a protective film on the actual seal is not cut. And compared to production using water jet technology, the seals can also be manufactured as one-sided or two-sided, self-adhesive flat seals.
Get in touch with us!
We perform best under pressure! Personalized advice for the highest demands and a fast delivery guarantee ensure your satisfaction. Contact our sealing experts.
We look forward to your inquiry."
Extrusion of profile seals
In the extrusion process, the raw materials are pressed through a nozzle under pressure and at potentially high temperatures (high-temperature extrusion). This process can also trigger chemical reactions, such as vulcanization. The extruded material that emerges takes on the cross-sectional shape of the nozzle and can be of theoretically any length.
This means that extrusion allows for the production of very long profile seals in one step, which are then cut to the desired length. Therefore, this method is particularly well-suited for producing profile seals in variable lengths and large quantities.
A common example of extruded profile seals are silicone seals, which are used in windows, door frames, cars, etc.
This technique is also employed in the manufacture of inflatable seals. The extruded tubes are subsequently vulcanized together to form a ring.
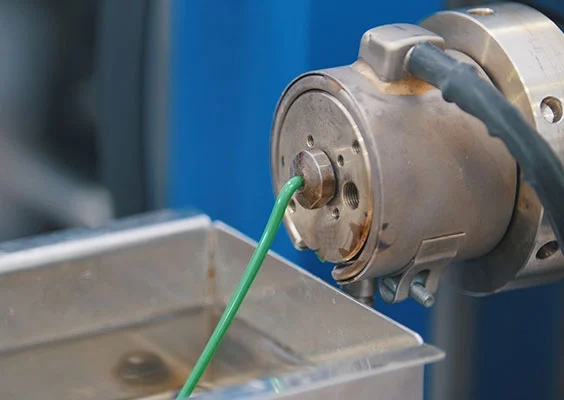

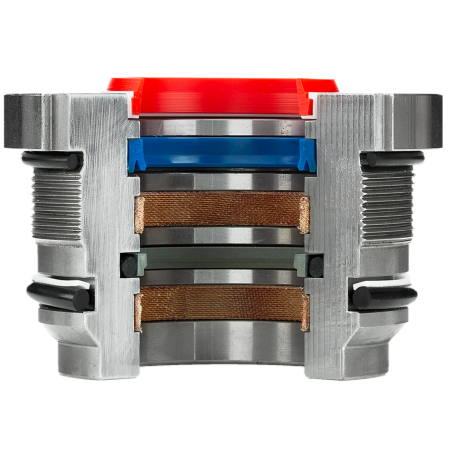
Injection moulding
In the injection molding process, raw materials are melted by heating, mixed together, and then injected into a mold under pressure. There, the material solidifies through cooling or a chemical cross-linking reaction. Once the material is solid, the mold opens, and the molded part is ejected. Often, the workpiece needs to be separated from the sprue and deburred.
With today's injection molding technology, very complex molded parts are achievable. Additionally, the surface texture can be customized to almost any specification: smooth, rough, ribbed, etc.
Particularly relevant for seals are rubber components made from elastomers, such as O-rings, scrapers, or groove rings suitable for hydraulic and pneumatic applications, which can be manufactured through injection molding.
Common materials include:
- NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber)
- Viton® (FPM, FKM - fluorocarbon rubber)
- EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber, M-class)
- Silicones
This method can operate fully automatically, allowing for rapid production of large quantities. However, introducing a new workpiece can be quite complex, leading to high initial investment costs and a long production time, which, for large volumes, are significantly offset in the long term. Kofler - Dichtungen also produces hydraulic seals and pneumatic seals. Additionally, our range includes Simmering seals.


Get in touch with us!
We perform best under pressure! Personalized advice for the highest demands and a fast delivery guarantee ensure your satisfaction. Contact our sealing experts.
We look forward to your inquiry."
