-
Homepage
-
Sealing knowledge
- What seals really need to accomplish
What seals really have to accomplish
Sealing technology is continually innovating new types of seals and gaskets, having developed an array of seals for specific application areas to date.
Among other functions, seals are designed to ensure the efficiency and safety of systems, providing optimal integration and sealing of various components.
At first glance, the technical characteristics of seals might appear complex due to the numerous varieties of seals and seal sets available in different materials.
Just as every pot has its matching lid, every performance system has its corresponding seal. This article aims to offer you a glimpse into the world of seals and highlight the fundamental benefits of seals.
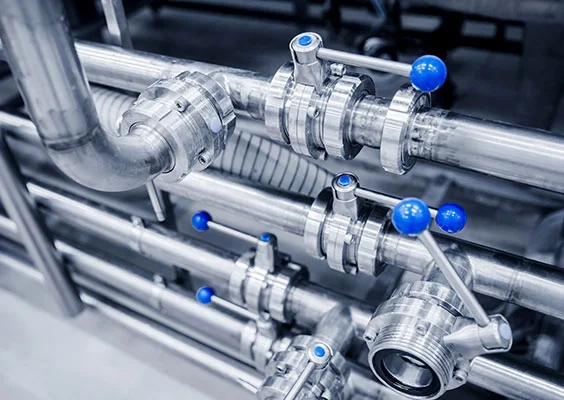

Where are seals and gaskets being used?
Whether in large systems, simple hydraulic cylinders or pneumatic cylinders, metering systems, pipe connections, grinders and much more – seals and gaskets can be found almost everywhere in a wide variety of shapes and materials. They meet a variety of different requirements and ensure that everything runs safely, efficiently and for a long time.
The field of application of seals extends from mega presses to automation systems to wood splitters in the private sector.
Even if many seals look mostly inconspicuous, their function is unavoidable for smooth operation.
What quality features must technical seals have?
For a high-quality seal or gasket, the choice of technical material is one of the most crucial performance characteristics. Additionally, a precisely manufactured geometry and surface finish are vital for the integrity of a high-quality seal.
A seal should exhibit no imperfections - such as holes, blisters, or scratches - and the technical material used must be of superior quality. Given their high material density, seals are expected to maintain a certain level of elasticity.
In the case of the so-called "compression set," compressed elastomer seals must revert to their original shape, a process also referred to as "rebounding." This capability is fundamental for a seal's functionality, offering protection against potential leaks of pressurized media.
An illustrative example would be the seal lips on retaining rings. The quality of this type of sealing element can be assessed by its round, clean, and intact appearance.

Seals for high pressure
For high-pressure applications, seals incorporate specific geometries and shapes. Seals made from elastomers, such as piston seals and rod seals from PU, can be equipped with an additional backing ring made of a technical plastomer (POM) to prevent gap extrusion.
Seals that must endure high pressure are typically fabricated from harder elastomers (e.g., NBR 90°). Extremely high pressures, such as those encountered in hydrostatic presses, necessitate that the industrial seals employed are of outstanding quality and made from the most advanced materials.
Seals and Gaskets for special substances
The material of a seal or gasket is particularly important in the food industry, pharmaceutical industry, heavy industry and chemical industry. In these areas, very aggressive substances can occur, which the seal must withstand.
Examples of appropriately resistant sealing materials are FKM (Viton®, fluorinated rubber) or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene). These are often used in the above-mentioned industries, but there are also other, highly technical materials.
Particularly in the food industry, care must also be taken to ensure that the material may come into contact with food and that contact does not impair the smell or taste of the food.
In addition, the seal must be approved by the FDA (within the EU also: EU1935/2004). The FDA carefully checks that only harmless materials are used in food production. For example, there are special Teflon seals for filling systems.
Seals for high and low temperatures
Just like with special substances, high and low temperatures also present a challenge that a seal or gasket must overcome. Regardless of the temperature, a seal must maintain its technical properties.
Materials well-suited for high and low temperatures include PTFE and FKM. For applications in low temperatures, for example, low-temperature polyurethane or silicone (MVQ) is appropriate. At high temperatures, such as those found in blast furnaces, flat graphite gaskets or mica materials are utilized.
Get in touch with us!
We perform best under pressure! Personalized advice for the highest demands and a fast delivery guarantee ensure your satisfaction. Contact our sealing experts.
We look forward to your inquiry."
Seals for special movements
Seals are also utilized for rotational movements or swift lifting actions, employing special materials and geometries designed to endure high mechanical stresses. Often, for shaft seals (Simmerring seals), unique forms are found, or self-lubricating materials such as PU-MoS2 are used for other types of rotary seals. Due to their excellent sliding properties, Teflon seals are frequently used for lifting movements. These seals, preloaded as O-ring mechanical seals, are commonly found in many hydraulic cylinders.
Hydraulic seals and pneumatic seals
In contrast to pneumatics, which perform mechanical work with compressed air, hydraulics operate with fluid that is usually under high pressure.
A hydraulic seal is thus utilized to isolate the hydraulic fluid from its environment and to prevent the leakage of hydraulic fluid, as well as to avoid the infiltration of air, dirt, and dust. What exactly are hydraulic seals?
Pneumatic seals are primarily used in situations where high pressures are not present. A pneumatic seal's role is also to shield the system from incoming dirt and moisture, largely thanks to the wiper located behind the seal.
Pneumatic systems impose special demands on seals because the friction conditions and the medium differ between hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Therefore, the shape and design of a seal are specifically tailored for its application in the hydraulic or pneumatic domain.

Custom Seals - Continuous Technological Advancement
With our custom-made special seals, we can specifically address your problems and requirements. Thanks to years of experience, know-how and the use of state-of-the-art designs and materials, every individual requirement of a product from various industrial sectors can be offered.
There are various possibilities for the production of seals. Flat gaskets are usually punched or cut with a water jet. Profile seals, on the other hand, are moulded or turned.

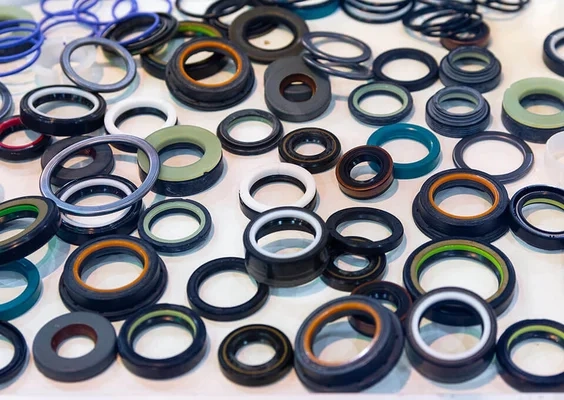
Materials in Sealing Technology
Numerous high-performance sealing materials have been developed to cover the wide range of applications with their individual requirements. The range of material properties with regard to hardness, elasticity, chemical resistance, operating temperature, electrical insulation properties and much more has become very large.
For virtually any application, the ideal material can be selected from several options, e.g. PU, NBR or PTFE compounds for piston seals for hydraulic cylinders.
- NBR – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber
Resistant to greases and oils, water up to approx. 100°C (212°F)
- FKM (FPM) – Fluorine Rubber
Resistant to various chemicals and high temperatures up to approx. 200°C (392°F)
- EPDM – Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber
Resistant to ozone and brake fluid
Temperature resistance between -45°C and +130°C (-49°F and +266°F)
- VMQ (MVQ) – Silicone Rubber
aging and weather resistant
Temperature resistance between -55°C and +200°C (-67°F and 392°F)
- PU – Thermoplastic Polyurethane
High strength and resistance to wear and extrusion
Resistant to fats and oils
Temperature resistance between -30°C and +100°C (-22°F and 212°F)
- PTFE – Polytetrafluoroethylene
High media resistance and sliding properties
Temperature resistance between -200°C and +250°C (-328°F and 482°F)
- POM – Polyoxymethylene
Sliding material with high compressive and extrusion strength, very good machinability, with very low water absorption.
Temperature resistance between -45°C and +100°C (-49°F and +212°F)


Get in touch with us!
We perform best under pressure! Personalized advice for the highest demands and a fast delivery guarantee ensure your satisfaction. Contact our sealing experts.
We look forward to your inquiry."
